“Measurement of blood pressure changes associated with postural change is a common parameter used in a select group of ED patients as an adjunct in the assessment of volume status, hemodynamic stability, and medication toxicity. Orthostatic hypotension has been defined by a consensus statement developed by the American Academy of Neurology and American Autonomic Society as a decrease in systolic blood pressure of > 20 mm Hg or a diastolic drop > 10 mm Hg within 3 min of going from a supine to a standing position” (Guss)
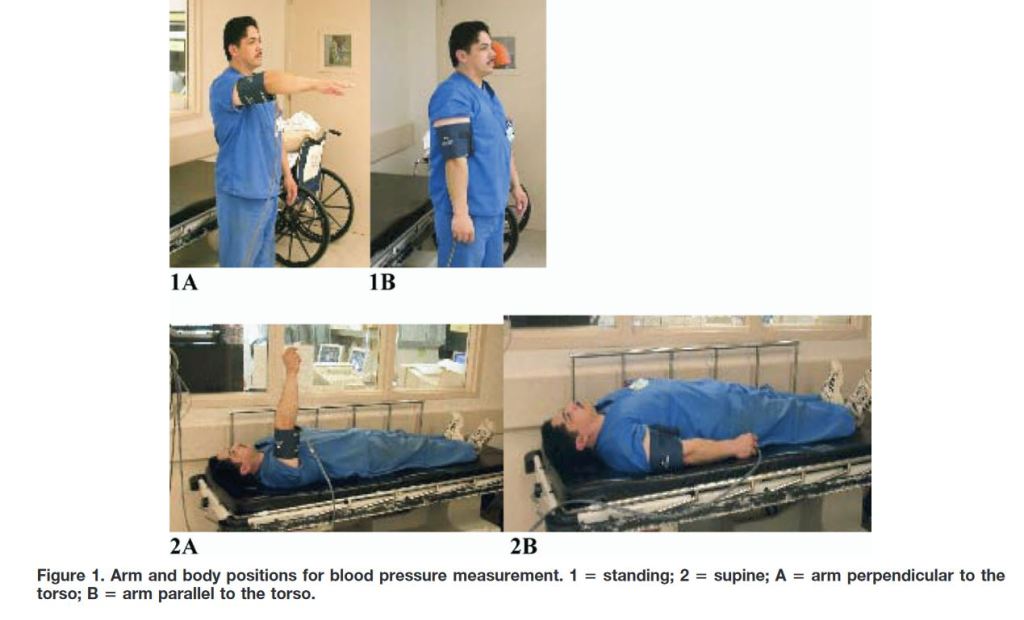
Guss, D. A., Abdelnur, D., & Hemingway, T. J. (2008). The impact of arm position on the measurement of orthostatic blood pressure. The Journal of emergency medicine, 34(4), 377-382.
Continue reading