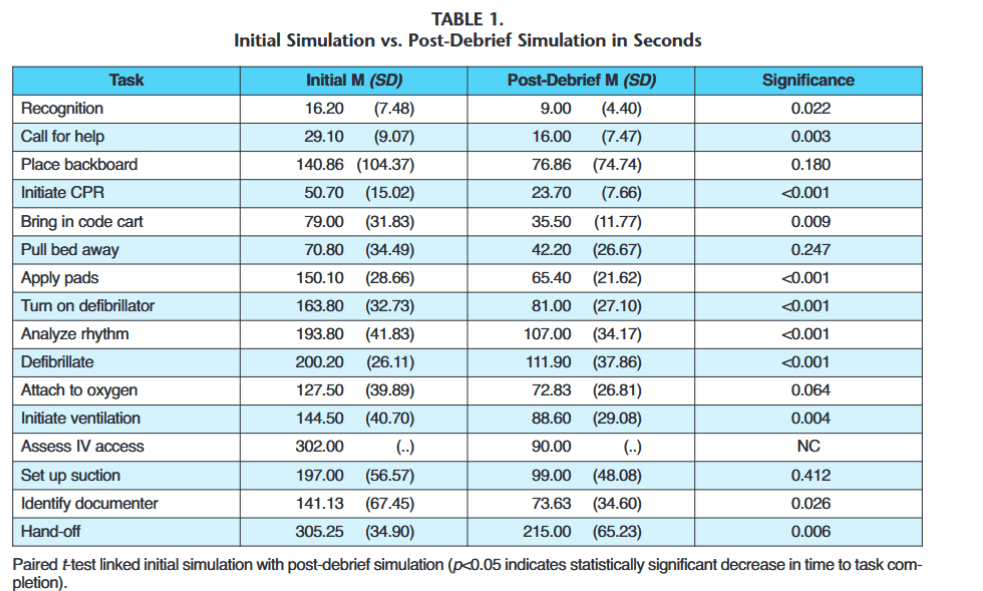
“Premature infants have an underdeveloped epidermal barrier with few cornified layers increasing their risk for greater permeability by noxious agents, high water loss, delayed skin maturation, skin damage, and infection. Their skin is easily torn due to deficiency of dermal structural proteins. Stratum corneum (SC) maturation is rapid upon exposure to a dry environment. At 23 weeks, it is nearly absent, with transepidermal water loss (TEWL) of
75 g/m 2 /h. By week 26, a few cornified layers have formed (TEWL of ~45 g/m 2/h), corresponding essentially to a wounded skin surface. One month later, premature SC was not fully competent, as indicated by significantly higher TEWL (17 g/m 2 /h) than normal, full-term infants. Complete skin maturation may take as long as 9 weeks and longer for complete acid mantle formation.”
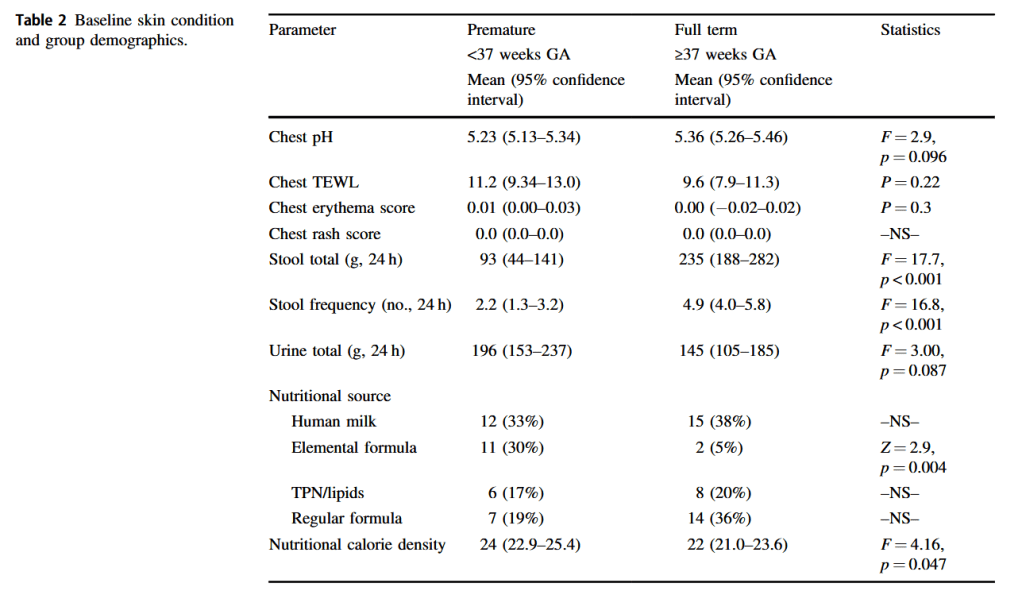
Visscher, M. O., Carr, A. N., & Narendran, V. (2021). Premature infant skin barrier maturation: status at full-term corrected age. Journal of Perinatology, 41(2), 232–239.
Continue reading