“Opioids are vital to pain management and sedation after trauma-related hospitalization. However, there are many confounding clinical, social, and environmental factors that exacerbate pain, post-injury care needs, and receipt of opioid prescriptions following orthopaedic trauma. This retrospective study sought to characterize differences in opioid prescribing and dosing in a national Medicaid eligible sample from 2010–2018. The study population included adults, discharged after orthopaedic trauma hospitalization, and receiving an opioid prescription within 30 days of discharge.”
Continue readingCategory Archives: Pain Management
Music therapy for pain and anxiety
“There is little research on the use of music therapy with pediatric chronic pain conditions such as amplified pain syndromes. The purpose of the current study was to examine the effects of 3 specific music therapy interventions (active music engagement, live patient-selected music, and music-assisted relaxation) on anxiety and relaxation levels in youth
(ages 10–18) participating in a 40 hr per week hospital-based intensive interdisciplinary pain treatment program.”
“Results show that when utilized within an interdisciplinary treatment environment, specific music therapy interventions elicited positive changes in relaxation and current somatic and cognitive anxiety levels in youth with amplified pain syndromes. Replication of this project with a larger sample size and a control group would lead to more confidence in these preliminary findings”
Comparing Three Music Therapy Interventions for Anxiety and Relaxation in Youth With Amplified Pain.(includes abstract) Scheufler, Ashley; Wallace, Dustin P; Fox, Emily Journal of Music Therapy, Summer2021; 58(2): 177-200. 24p
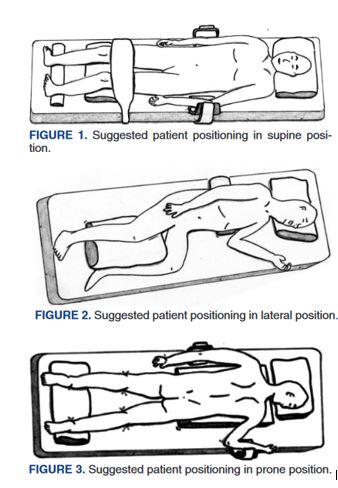
Continue readingPrevention of pressure ulcers for patients undergoing endoscopy procedures.
“Patient positioning during gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures has received minimal attention compared with surgical procedures performed in the surgical setting. However, prolonged endoscopic interventions on patients and the increasing requirement for general anesthesia have changed to need for patient positioning guidelines. It is crucial to establish positioning guidelines for endoscopic procedures in supine, prone, and lateral positions.
These new patient positioning guidelines during gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures should become part of national endoscopy practice standards and the education curriculum of endoscopy nurses.” (Meeusen)
What is the required or recommended nursing documentation for patients in the pre-operative and post-operative phases?

Santos Almeida, A. C., et al (2021). Inadequate completion of surgical data for patient safety: opinion of health professionals. Rev Rene, 22(1), 1–8. Free Full Text
Grommi, S., et al (2021). Educating Registered Nurses for Pain Knowledge and Documentation Management: A Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Caring Sciences, 14(2), 919–929. Full Text for Emory Users
Lakshmikantha, N., & Lakshman, K. (2021). A Review of Operation Theater Notes in a Tertiary Care Center. Indian Journal of Surgery, 83(4), 956–959. Full Text for Emory Users
Shoqirat, N., et al (2019). Nursing Documentation of Postoperative Pain Management: A Documentary Analysis. Journal of Nursing Care Quality, 34(3), 279–284. Full Text for Emory Users
Using ice to prevent mouth sores during chemotherapy.
Reis, Paula; Ciol, Marcia; Melo, Nilce; Figueiredo, Paulo; Leite, André; Manzi, Natália; Dos Reis, Paula Elaine Diniz; Ciol, Marcia A; de Melo, Nilce Santos; Figueiredo, Paulo Tadeu de Souza; Leite, André Ferreira; Manzi, Natália de Melo Chamomile infusion cryotherapy to prevent oral mucositis induced by chemotherapy: a pilot study. Source: Supportive Care in Cancer (SUPPORT CARE CANCER), Oct2016; 24(10): 4393-4398. (6p)
Karagözoglu S; Ulusoy MF Chemotherapy: the effect of oral cryotherapy on the development of mucositis.
Journal of Clinical Nursing (J CLIN NURS), Jul2005; 14(6): 754-765. (12p)
Nikoletti S; Hyde S; Shaw T; Myers H; Kristjanson LJ Comparison of plain ice and flavoured ice for preventing oral mucositis associated with the use of 5 fluorouracil. Journal of Clinical Nursing (J CLIN NURS), Jul2005; 14(6): 750-753. (4p)
Taheri JB; Razavi SM; Hajir S; Vaziri P; Bakhtiari S Effect of local hypothermia in prevention or reduction of chemotherapy induced mucositis signs.
Journal of Dental School (J DENT SCH), 2009 Autumn; 27(3): 6-6. (1p)
Katrancı, Nilgün; Ovayolu, Nimet; Ovayolu, Ozlem; Sevinc, Alper Evaluation of the effect of cryotherapy in preventing oral mucositis associated with chemotherapy – A randomized controlled trial.
European Journal of Oncology Nursing (EUR J ONCOL NURS), Sep2012; 16(4): 339-344. (6p)
Wodzinski, Amelia Potential Benefits of Oral Cryotherapy for Chemotherapy-Induced Mucositis.
Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing (CLIN J ONCOL NURS), Oct2016; 20(5): 462-465. (4p)
Use of PCA pump for pain management of sickle cell patients in the emergency room.
Cho, G., Anie, K., Buckton, J., Kiilu, P., Layton, M., Alexander, L., . . . Meredith. (2016). SWIM (sickle with ibuprofen and morphine) randomised controlled trial fails to recruit: Lessons learnt. BMJ Open., 6(6), E011276.
Kavanagh, P., Sprinz, P., Wolfgang, T., Killius, K., Champigny, M., Sobota, A., . . . Moses, J. (2015). Improving the Management of Vaso-Occlusive Episodes in the Pediatric Emergency Department. Pediatrics /, 136(4), E1016-E1025.
Telfer, P., Bahal, N., Lo, A., & Challands, J. (n.d.). Management of the acute painful crisis in sickle cell disease- a re-evaluation of the use of opioids in adult patients. British Journal of Haematology., 166(2), 157-164.
Uprety, D., Baber, A., & Foy, M. (n.d.). Ketamine infusion for sickle cell pain crisis refractory to opioids: A case report and review of literature. Annals of Hematology., 93(5), 769-771.
Emergency provider analgesic practices and attitudes toward patients with sickle cell disease. (2013). Annals of Emergency Medicine : Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians., 62(4), Annals of emergency medicine : journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians. , 2013, Vol.62(4).
What is the effect of music therapy on pain (or stress reduction) during dressing changes?
The majority of search results focused on music therapy reducing pain or stress during dressing changes in burn patients.
Evidence Summaries
Joanna Briggs
Burns Pain (Adults): Non-Pharmacological Management. Miller, Kate [BOccTh PhD]. Kipping, Belinda [BOccTh MPhil]. Gray, Paul [MBBS PhD FANZCA FFPMANZCA]. Schug, Stephan. Munn, Zachary [PhD]. [Recommended Practices] 2014
This study reports that generally there is a lack of high quality evidence for nonpharmacological interventions reducing stress or pain in burn patients.
Literature search in PubMed was more specific to music therapy:
My search strategy was (“Bandages”[Mesh] OR bandages OR biological dressings OR occlusive dressings) AND music therapy AND (pain OR stress)
See addititonal PubMed references by clicking on this link:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/myncbi/collections/public/1PQtun_Aiz3ViSsu-3u3inwQm/
Searching other databases like CINAHL and PsycINFO did not produce any new results.
See also this post in the blog:
Effectiveness of music therapy as an adjunct to pharmacological pain relief in post-op patients
