“Health care workers (HCWs) are presumed to be athigh risk for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)through occupational exposure to infected patients orcoworkers. Studies have reported a wide range of sero-prevalence of severe acute respiratory syndrome corona-virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes COVID-19,among HCWs. This variation has in part been attributedto differential risk for exposure in the community. Indeed, recent studies have shown that a substantialnumber of infections among HCWs could not be tracedto occupational exposures and that community expo-sures were as or more strongly associated with infection.”
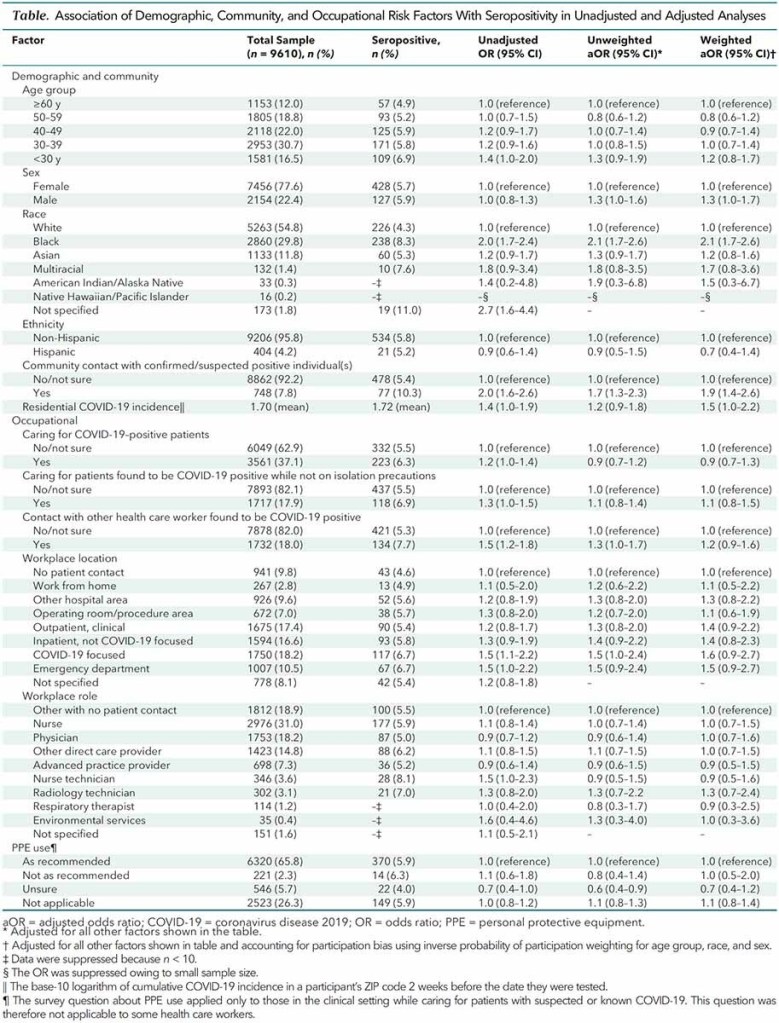
‘In conclusion, using a model incorporating demographic, community, and occupational risk factors for infection, we quantified community and occupational risk for SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity in HCWs. We found that the largest predictors of risk related to community exposure; ongoing efforts to keep the health care workforce safe should emphasize risk mitigation in and outside the workplace. After adjustment for many community and occupational risk factors, race remains a critical marker of infection risk. Future seroprevalence studies of HCWs need to account for these community and demographic factors.”
Baker JM, et al. Quantification of Occupational and Community Risk Factors for SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity Among Health Care Workers in a Large U.S. Health Care System. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2021;174(5):649-654.
